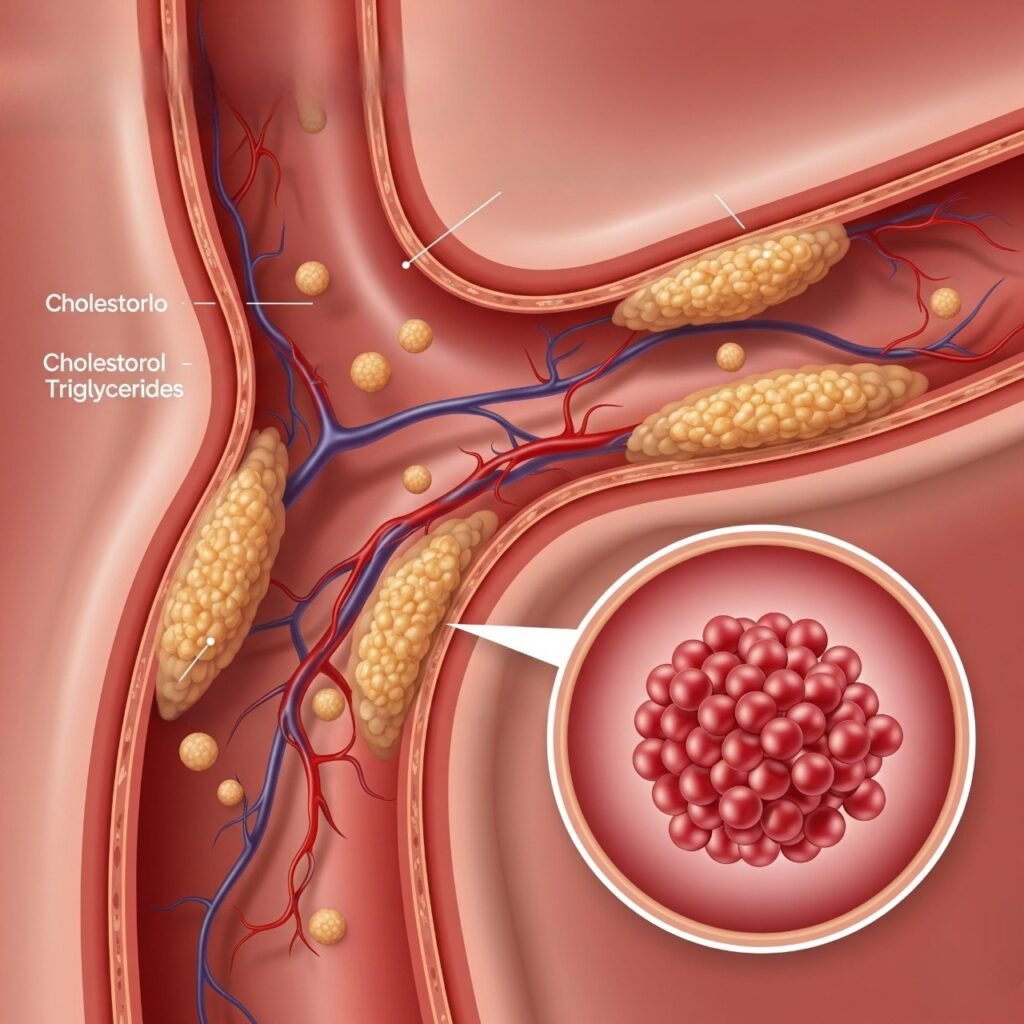
Dyslipidemia Treatment
Managing dyslipidemia is essential to lowering the risk of heart attack and stroke. The foundation of treatment lies in lifestyle changes—eating a balanced, heart-healthy diet full of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and good fats, while limiting saturated fats, trans fats, and sugars. Regular physical activity (at least 30 minutes most days), weight control, avoiding tobacco, and limiting alcohol are key steps. If lifestyle efforts aren’t enough, medications like statins, fibrates, or cholesterol absorption inhibitors may be prescribed to manage LDL, HDL, and triglyceride levels. Ongoing blood tests and doctor visits help keep the condition in check.
IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) Treatment
IBS is managed by easing symptoms rather than curing the condition. Dietary changes often help—such as smaller, more frequent meals and avoiding known triggers like caffeine, fatty foods, and some sweeteners. A low FODMAP diet may be beneficial. Since stress can worsen IBS, techniques like meditation, exercise, and therapy are helpful. Depending on whether symptoms lean toward diarrhea or constipation, doctors may use antispasmodics, laxatives, antidiarrheals, or specific antidepressants. Supplements like fiber and probiotics might also offer relief. Treatments are tailored over time, based on individual symptom patterns.
